- The Babylonians divided a day into 24 hours, an hour into 60 minutes and a minute into 60 second. They also divided a complete revolution into 360 degrees.
- Amazingly, these measurement conventions are still widely used today and they suit well in Babylonian number system, which is a base 60 positional system.
- You can see that Babylonian number system does not have a "zero". The absence of zero sometimes causes ambiguity when writing numbers in Babylonian numerals.
Let's consider the following example:
Example 2.3.
How to represent "3601" in Babylonian numerals? It turns out that it is written as "1", one "empty space" and "1". However, it can easily be confused with "61", which is written as two "1"s.
Similar problem occurs when one wants to represent "21601" in Babylonian numerals. It is supposed to be expressed as "1", two "empty spaces" and "1". However, it's really hard to distinguish between one and two empty spaces.
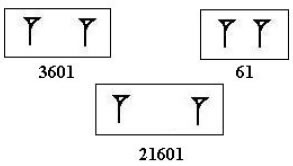
Three examples
Therefore, sometimes one needs to look into the context to resolve this ambiguity. It turns out that later Babylonian civilisations did invent a symbol for an empty space. We will talk more about the invention of zero in later lesson.
~ End of Lesson ~