Babylonian number system is a base 60 positional system (it is also called sexagesimal number system). But Babylonians did not use 59 different symbols to represent 59 different digits (zero was missing in Babylonian number system). The following is the table of all 59 different Babylonian numerals:

Table of all Babylonian numerals
Credit: Wikipedia
From the table, you can see that all these 59 numerals are built from two simple cuneiform symbols – "Y" represents 1 and "<" represents 10. Since Babylonian number system is a base 60 positional system, "Y" can also represent 60, 602, 603 ,and other powers of 60, depending on the position of "Y". How about "<" ? What other numbers can "<" represent?
The following are some examples of numbers in Babylonian numerals:
Example 2.2.
What are these numbers?
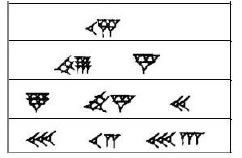
Numbers in Babylonian numerals
Credit: Queen’s University, Math@Home 2001-2002
1. 15
2. 59 × 601 + 5 = 3545
3. 8 × 602 + 45 × 601 + 20 = 31520
4. 30 × 602 + 12 × 601 + 33 = 108753